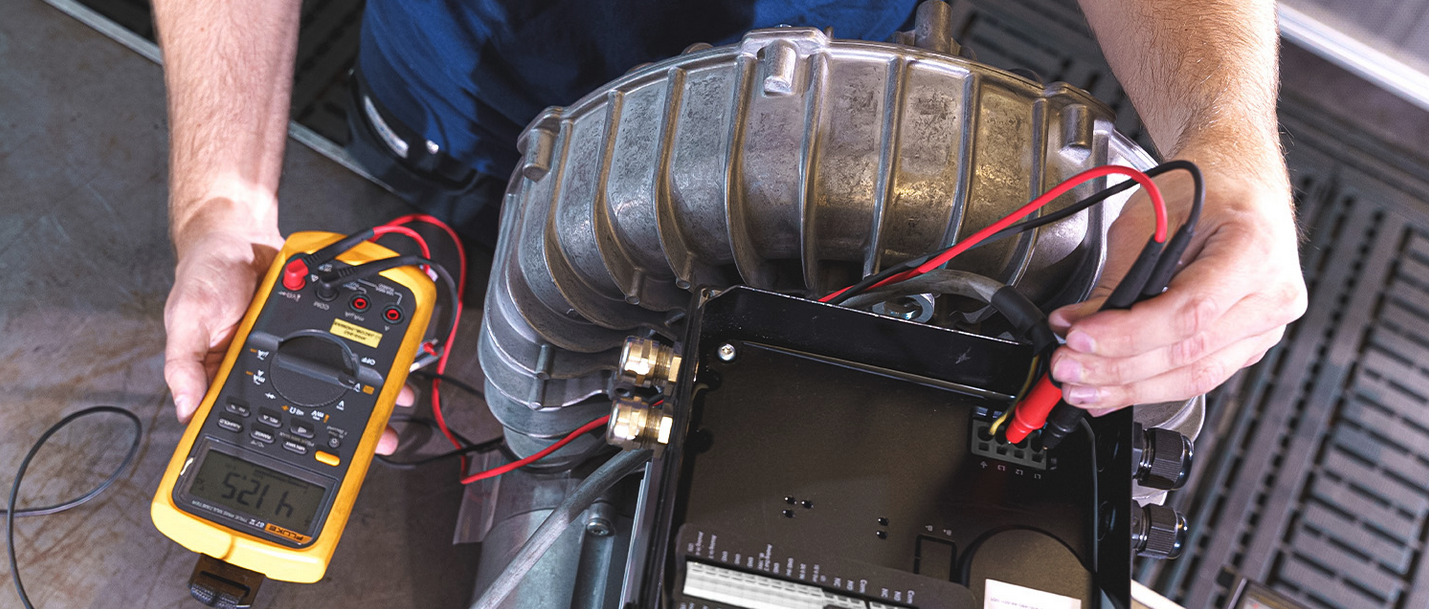
How to Test a Vacuum Pump with Bobcat Industrial Air Services
At Bobcat Industrial Air Services in Nashville, TN, we understand that regular testing of vacuum pumps is essential to maintain peak performance, prolong equipment life, and avoid costly downtime. Whether your vacuum pump powers critical lab experiments or industrial processes, implementing a robust testing routine is vital to catching issues early and ensuring reliable operation.
Why Test Your Vacuum Pump Regularly?
Vacuum pumps often operate continuously and rely on wearable parts to maintain performance. Without regular testing, minor issues can escalate into significant problems, including:
Increased energy consumption
Damage to internal components
Costly repairs or replacements
Catastrophic failure during critical operations
By testing your pumps, you ensure they operate efficiently, extend their lifespan, and avoid unexpected breakdowns that can disrupt essential operations.
How Often Should You Test Your Pump?
The frequency of vacuum pump testing depends on:
Application criticality: Pumps in hospitals or labs should be tested frequently due to the high stakes of failure.
Operating conditions: Pumps in extreme temperatures, dusty environments, or running at maximum capacity require more frequent checks.
Usage: High-use pumps should be tested more often than those used intermittently.
Bobcat Industrial Air Services recommends testing pumps after a set number of operating hours based on the manufacturer’s guidelines and specific environmental factors.
Benefits of Regular Vacuum Pump Testing
Preventative Maintenance: Catching minor leaks, wear, or overheating early prevents more serious issues.
Cost Savings: Proper testing avoids energy waste and reduces the need for emergency repairs.
Optimal Performance: Testing ensures your pump operates at its rated vacuum levels and flow capacity.
Prolonged Equipment Life: Routine checks help you perform maintenance tasks like oil changes and filter replacements on time.
How to Test Your Vacuum Pump
Manual Inspection
Start with a hands-on approach to detect visible and audible signs of wear:
Visual Check: Inspect hoses, power cords, and pump housing for damage.
Oil Inspection: For oil-lubricated pumps, check the oil level and look for signs of burning, such as darkened oil or a burned odor.
Filter Check: Ensure external or integrated filters are clean and unclogged. Replace filters if necessary.
Run the Pump: Listen for unusual noises, feel for vibrations, and check the vacuum pressure gauge. Ensure the pump reaches its rated vacuum level by measuring close to the inlet.
Diagnostic Testing
A diagnostic test provides more precise insights into your pump’s health:
Gather Tools: Vacuum gauge, flat plate or adapter, clamp amp probe, and any necessary hand tools.
Isolate the Pump: Disconnect it from the system.
Connect the Gauge: Attach it to the inlet port.
Test the Vacuum Level: Run the pump and compare the vacuum reading to the rated specs on the pump’s plate.
Check Amperage: Measure the pump’s amperage with a probe. Ensure it is at or below the full load amps (FLA) listed on the motor tag.
When to Call the Experts
Even with routine testing, some issues require professional attention. At Bobcat Industrial Air Services, we offer comprehensive vacuum pump diagnostics and maintenance services. Our team can help:
Address abnormal readings, such as excessive amperage or reduced vacuum levels.
Perform advanced repairs for overheating or worn components.
Optimize your system for improved performance and efficiency.
Why Choose Bobcat Industrial Air Services?
Bobcat Industrial Air Services in Nashville, TN, is your trusted partner for all things vacuum pump-related. We provide:
Expert Guidance: From testing and diagnostics to repairs, our team ensures your pumps are in peak condition.
Top-Quality Products: We offer industry-leading vacuum pump systems tailored to your needs.
Preventative Maintenance Programs: Stay ahead of issues with scheduled testing and servicing.
Contact Us Today
Ensure your vacuum pumps perform reliably and efficiently with help from Bobcat Industrial Air Services. Contact us for testing support, maintenance, and expert advice to keep your operations running smoothly.
Exploring the Common Uses of Vacuum Pumps in Laboratories with Bobcat Industrial Air Services
Laboratory environments depend heavily on vacuum technology to perform a wide variety of essential processes, from filtering mixtures to evaporating solvents. At Bobcat Industrial Air Services in Nashville, TN, we provide tailored vacuum solutions to meet the specific demands of laboratories, ensuring efficiency, reliability, and optimal performance.
How Vacuum Pumps Support Laboratory Applications
Vacuum pumps are vital for creating and maintaining low-pressure environments essential for many lab processes. Whether it's testing and calibration, cell culture growth, or solvent evaporation, the right vacuum pump is critical for accurate and efficient operation. However, selecting the wrong pump for an application can result in reduced performance, increased maintenance, or even equipment damage.
Key Laboratory Applications for Vacuum Pumps
1. Membrane Filtration
Vacuum filtration accelerates the separation process by creating a pressure drop that forces liquid through a filter membrane.
Critical Factor: Pumping speed for faster evacuation times.
Bobcat Solutions: Our rotary vane vacuum pumps are ideal for achieving quick pump-down times and necessary vacuum levels for filtration.
2. Aspiration
Vacuum is used to remove fluids or gases from containers, such as collecting samples or removing waste.
Critical Factor: Pumping speed and suction control to handle varying fluid volumes without damaging samples.
Bobcat Solutions: For wet applications, our lubricated vacuum pumps ensure smooth operation and prevent contamination.
3. Distillation and Rotary Evaporation
These processes purify liquids by lowering their boiling points under vacuum, enabling evaporation at reduced temperatures.
Critical Factor: Ability to handle vapor ingestion without reducing vacuum efficiency.
Bobcat Solutions: Our oil-sealed rotary vane pumps, equipped with gas ballast valves, handle vapor ingestion effectively, maintaining reliable operation.
4. Degassing
Vacuum pumps remove gases from liquids to eliminate air bubbles that could interfere with testing or analysis.
Critical Factor: Maintaining a deep, continuous vacuum.
Bobcat Solutions: Our rotary vane pumps achieve deep vacuum levels (1.5–0.075 torr), ensuring efficient degassing for most lab applications.
5. Analysis Equipment
Vacuum environments are critical for precision testing in applications such as mass spectrometry and chromatography.
Critical Factor: Application-specific requirements, including oil-free operation or ultra-high vacuum levels.
Bobcat Solutions: While we supply pumps suitable as backing systems for ultra-high vacuum units, our rotary claw and oil-free systems are ideal for contamination-sensitive applications.
Advantages of Bobcat’s Laboratory Vacuum Systems
At Bobcat Industrial Air Services, we ensure that your laboratory vacuum pumps are not only functional but also optimized for your unique needs.
Customized Solutions
From centralized vacuum systems to individual units, we provide pumps designed to handle various applications simultaneously. Our team helps you balance capacity, scalability, and efficiency.
Noise Reduction
Our advanced pump systems, including the oil-lubricated U5 series, are engineered for quieter operation—ideal for smaller lab setups where noise can disrupt workflow.
Energy Efficiency
Many lab processes demand continuous operation. Our pumps are designed to operate at maximum efficiency while meeting energy and sustainability goals.
How Bobcat Can Help
Our expertise allows us to guide you in selecting the right vacuum pump for your lab:
Determine application-specific needs, such as pumping speed, vacuum depth, and flow rates.
Recommend oil-sealed or oil-free options based on contamination risks and operating conditions.
Design systems that combine central vacuum systems with individual pumps for maximum flexibility.
Why Choose Bobcat Industrial Air Services?
Located in Nashville, TN, Bobcat Industrial Air Services is committed to providing top-tier vacuum solutions for laboratories. With our comprehensive product lineup and industry expertise, you can trust us to deliver reliable, efficient, and cost-effective vacuum systems tailored to your operations.
Contact Us Today
Reach out to Bobcat Industrial Air Services for expert advice on laboratory vacuum pump solutions. Let us help you equip your lab with pumps designed to optimize performance, reduce downtime, and support your most critical applications.
How to Choose the Right Size Laboratory Vacuum Pump with Bobcat Industrial Air Services
At Bobcat Industrial Air Services in Nashville, TN, we understand that laboratory efficiency depends on reliable, well-sized vacuum systems. From small educational labs to large research facilities, ensuring your vacuum pump is tailored to your needs is essential for smooth operation, cost-efficiency, and safety. This guide walks you through the key factors to consider when selecting the right size laboratory vacuum pump and how Bobcat Industrial Air Services can help you make the best choice.
Why Proper Vacuum Pump Sizing Matters
Selecting the correct size vacuum pump is crucial for achieving optimal performance and maintaining the integrity of your lab processes. Oversized or undersized pumps can lead to operational inefficiencies and costly damages:
Oversized Pumps: These can cause poorly controlled evacuation, risking equipment damage or contamination due to unwanted gas release. They also consume excess energy, increasing operational costs.
Undersized Pumps: These may struggle to maintain the necessary vacuum level, delaying processes and reducing efficiency, potentially damaging the pump itself over time.
Bobcat Industrial Air Services helps you balance capacity and efficiency, ensuring your pump is optimized for both high-demand and average-use scenarios.
Key Factors in Sizing a Laboratory Vacuum Pump
Here’s what to evaluate when sizing your pump:
1. Desired Vacuum Level
Determine the vacuum level required for your application. Whether it’s a low-level vacuum for small-scale tasks or a sustained, deep vacuum for advanced research, Bobcat can recommend solutions to meet your needs.
2. Flow Rate
Flow rate determines how quickly your pump reaches the desired vacuum level. Consider factors like gas volume and site elevation, as higher altitudes may reduce pump efficiency.
3. Application Type
Decide whether your vacuum pump will serve a single application or a centralized system supporting multiple stations. Centralized systems require greater capacity and redundancy.
4. Redundancy Requirements
Incorporate additional capacity to handle unexpected demand spikes, minor leaks, or pump downtime. At Bobcat, we can design systems with modular components to ensure uninterrupted performance.
5. Energy Efficiency
Meeting energy efficiency and sustainability goals is increasingly important. Bobcat offers energy-efficient pumps that balance performance with reduced power consumption.
6. Service Factor
Consider how frequently your system will operate at peak demand. If usage is intermittent, you may not need the same capacity as a system running continuously.
Bobcat’s Recommended Vacuum Pump Solutions
Bobcat Industrial Air Services provides cutting-edge vacuum systems designed for reliability and efficiency in laboratory settings.
Oil-Sealed Pumps
Our oil-sealed pumps are ideal for handling gases that might be ingested during evacuation. They pair well with vapor condensation filters to prevent corrosion and ensure safety.
Modular Centralized Systems
For larger labs, we recommend modular setups like the Advantage-P Oil-Flooded Central Vacuum Systems. These systems include:
Expandable configurations for scalability
Automatic controls for alternating and cascading operation
Flow capacities from 18 to over 2,600 SCFM
High-efficiency pumps for applications requiring up to 0.075 Torr vacuum levels
Dry Pumps
Dry rotor, hook and claw, and dry screw pumps are available for specialized conditions requiring oil-free operation or lower vacuum needs.
Steps to Size a Vacuum Pump
For Centralized Systems:
Calculate system-wide flow in SCFM based on 25” Hg pressure.
Count the number of vacuum terminals across your facility.
Use the formula:
Flow Required = [Number of Terminals] x [SCFM per Terminal] x [Use Factor/100]Add the totals for all laterals to determine the overall flow requirement.
Match the flow requirement to the specifications of an appropriate vacuum pump.
For Single-Point Applications:
Simply match the application’s required flow and vacuum level to a pump that meets those specifications.
Planning for Future Growth
If your lab plans to expand or upgrade, Bobcat Industrial Air Services can help design a system that scales with your operations. Adding capacity now ensures you’re prepared for future demands.
Avoid Common Sizing Mistakes
Ignoring Leaks: Account for pressure loss due to leaks in plumbing or fittings.
Skipping Redundancy: Include extra capacity to manage unexpected downtime or increased usage.
Underestimating Flow: Ensure your pump can handle peak demand, not just average usage.
Why Choose Bobcat Industrial Air Services?
Located in Nashville, TN, Bobcat Industrial Air Services specializes in high-quality vacuum systems tailored to your laboratory’s unique needs. With our expertise, you gain:
Customized Solutions: Pumps designed to fit your specific applications and growth plans.
Energy Efficiency: Systems that align with sustainability goals while lowering costs.
Comprehensive Support: Installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting assistance.
Contact Us
Ensure your laboratory’s vacuum system is reliable, efficient, and future-proof. Contact Bobcat Industrial Air Services in Nashville, TN, for expert guidance and top-tier products. Let us help you keep your lab running smoothly.
The Ultimate Guide to Water Pumps: Types, Applications, and Maintenance with Bobcat Industrial Air Services
At Bobcat Industrial Air Services in Nashville, TN, we understand the critical role water pumps play in various industries and daily life. From managing water resources in industrial facilities to maintaining consistent pressure in plumbing systems, water pumps are essential tools. Whether you're a homeowner, farmer, or industrial manager, knowing the basics of water pumps can save you time, money, and frustration.
This guide dives into the types of water pumps, their applications, installation tips, maintenance strategies, and how Bobcat Industrial Air Services can help you find the right solution for your needs.
What is a Water Pump?
A water pump is a device that moves water from one point to another, overcoming gravity, friction, or pressure. They are versatile and essential in applications like irrigation, drainage, and boosting water pressure.
At Bobcat Industrial Air Services, we specialize in offering reliable pump solutions for residential, agricultural, and industrial needs. Whether you require an electric, gas-powered, or solar pump, we ensure you find the right product for your specific application.
How Water Pumps Work
Water pumps convert mechanical energy into fluid motion. Depending on the type of pump, this energy might come from electricity, fuel, or solar power.
Example: In homes, water pumps maintain steady water flow and pressure, ensuring reliable plumbing.
In industries: Pumps handle heavy-duty tasks like cooling systems, wastewater management, and chemical transportation.
Common Types of Water Pumps
Centrifugal Pumps
Applications: Domestic water supply, industrial cooling, irrigation.
Advantages: Affordable, efficient, easy to maintain.
Bobcat's Recommendation: Ideal for large-scale water movement at minimal costs.
Submersible Pumps
Applications: Floodwater drainage, deep wells, sewage treatment.
Advantages: Quiet, efficient, resistant to cavitation.
Bobcat's Tip: Perfect for demanding environments requiring durable equipment.
Jet Pumps
Applications: Residential well systems, rural water supply.
Advantages: Effective for deep wells, versatile.
Why Choose Bobcat: We offer reliable jet pumps with tailored solutions for your needs.
Solar-Powered Pumps
Applications: Off-grid areas, sustainable irrigation.
Advantages: Eco-friendly, low operational costs.
Our Expertise: Bobcat can guide you in selecting energy-efficient, cost-effective solar pumps.
Positive Displacement Pumps
Applications: Chemical processing, food production.
Advantages: Handles high-viscosity fluids, consistent flow.
Bobcat's Selection: Designed for precision in specialized industries.
Applications of Water Pumps
Residential: Boosting water pressure, lawn irrigation, pool circulation.
Agricultural: Livestock watering, drainage, and irrigation systems.
Industrial: Cooling, wastewater management, and chemical transport.
Emergency: Flood control, dewatering construction sites, firefighting.
At Bobcat Industrial Air Services, we offer pumps designed to meet the unique needs of Nashville's diverse industries and communities.
Choosing the Right Water Pump
Consider the following factors when selecting a water pump:
Flow Rate: How much water do you need to move?
Head Height: How far must the pump lift the water?
Water Quality: Is the water clear or contains debris?
Power Source: Electric, gas, or solar?
Budget: Balance initial costs with long-term efficiency.
Our team at Bobcat Industrial Air Services helps you navigate these factors, ensuring you choose the most cost-effective and efficient pump.
Installation and Maintenance
Proper installation and maintenance are crucial to the longevity and performance of your water pump.
Installation Tips:
Choose a stable location to minimize vibrations.
Use appropriate plumbing materials.
Prime the pump before operation to prevent airlocks.
Maintenance Tips:
Inspect for wear and leaks regularly.
Keep intake filters clean.
Schedule seasonal checks to avoid performance drops.
Bobcat Industrial Air Services offers professional installation and maintenance support to keep your pumps running smoothly.
Why Bobcat Industrial Air Services?
As Nashville's trusted partner in industrial and residential solutions, we bring:
Expert Guidance: From selection to maintenance, we’re with you every step.
High-Quality Products: Our pumps are built for durability and efficiency.
Local Support: We understand the unique challenges of our community and provide tailored solutions.
Contact Us
Ready to find the perfect water pump for your needs? Reach out to Bobcat Industrial Air Services in Nashville, TN. We’re here to provide expert advice and unmatched service. Let us help you manage your water resources with ease and confidence.
Troubleshooting Your Pressure Boosting System for Optimal Performance
Pressure booster systems are vital across various applications, ensuring consistent water pressure in residential, commercial, and industrial settings. From enhancing customer comfort to supporting critical infrastructure like firefighting systems and irrigation, these systems play a pivotal role. At Bobcat Industrial Air Services in Nashville, TN, we understand the importance of maintaining and troubleshooting pressure booster systems to avoid downtime and maximize efficiency.
Why Troubleshooting Matters
Regular troubleshooting and maintenance of pressure booster systems help to:
Ensure Consistent Water Supply: Prevent interruptions in water delivery.
Prevent System Failures: Address minor issues before they escalate.
Enhance Efficiency: Maintain optimal performance for cost savings.
Minimize Safety Risks: Avoid system malfunctions that could pose hazards.
Meet Compliance Standards: Ensure the system adheres to regulations.
Extend System Longevity: Reduce wear and tear through proactive care.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting Tips
Understanding common problems and their solutions is key to keeping your booster system running smoothly:
Pump Fails to Start
Potential Causes: Electrical issues, motor faults, or operational errors.
Solutions: Inspect electrical connections, test the motor, and verify proper voltage supply.
Pump Fails to Turn Off
Potential Causes: System leaks, pressure switch malfunctions, or incorrect settings.
Solutions: Check for leaks in the system, recalibrate the pressure switch, and ensure settings match system requirements.
High Switching Frequency or Fluttering
Potential Causes: Improperly sized pressure tank, incorrect switch settings, or leaks.
Solutions: Verify tank size, recalibrate the pressure switch, and inspect for leaks.
Low or No Pressure
Potential Causes: Clogged filters, blocked pipes, air leaks, or mechanical failures.
Solutions: Clean or replace filters, clear blockages, check for air leaks, and inspect pump components.
Dry-Running Protection System Issues
Scenario 1: Pump shuts off even with water present.
Causes: Faulty sensors or incorrect calibration.
Solutions: Test and recalibrate sensors; inspect electrical connections.
Scenario 2: Pump continues running despite low water levels.
Causes: Sensor malfunctions or miscalibration.
Solutions: Replace faulty sensors and recalibrate the system.
Key Maintenance Practices
Proactive maintenance is essential to prevent issues and extend the life of your pressure booster system:
Inspect Electrical Connections: Ensure wires and components are secure and free of corrosion.
Calibrate Pressure Settings: Regularly verify pressure settings align with system requirements.
Inspect Mechanical Components: Check for wear on parts such as seals, impellers, and valves.
Test Sensors and Protection Systems: Ensure all safety mechanisms function correctly.
Conclusion
Troubleshooting and maintaining pressure booster systems are critical for ensuring consistent water pressure, reducing operational costs, and preventing unexpected failures. By addressing issues like sensor malfunctions, frequent cycling, or low pressure, you can optimize system performance and reliability.
At Bobcat Industrial Air Services in Nashville, TN, we specialize in servicing pressure booster systems to keep them running efficiently. Contact us today to learn how we can help you maintain peak performance and prevent costly repairs.
Powering Fluid Flow: Key Insights on Radial (Centrifugal) Pumps
Radial pumps, commonly known as centrifugal pumps, are a cornerstone of fluid transportation in industries ranging from water treatment to power generation. By converting rotational energy into fluid flow, these pumps provide a dependable and efficient solution for moving liquids. At Bobcat Industrial Air Services in Nashville, TN, we understand the critical role these pumps play in various applications and help businesses implement the best solutions for their needs.
Applications of Centrifugal Pumps
Centrifugal pumps are versatile and serve a wide array of industries:
Water Supply: Essential in municipal water systems, agricultural irrigation, and potable water distribution.
HVAC Systems: Circulate water in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning setups.
Wastewater Treatment: Transport and process water efficiently in treatment plants.
Industrial Processes: Move chemicals, liquids, and other materials in manufacturing and food processing.
Power Generation: Handle boiler feed applications and cooling water circulation in power plants.
Advantages and Limitations of Centrifugal Pumps
Advantages:
Efficient Fluid Handling: Ideal for consistent flow at moderate pressures.
Wide Application Range: Adaptable to a broad spectrum of liquids and operating environments.
Low Maintenance Needs: Simpler design with fewer moving parts compared to other pump types.
Limitations:
Pressure Constraints: Best suited for moderate pressures; less effective at extremely high pressures.
Viscous Fluids: Performance declines with high-viscosity fluids due to reliance on fluid velocity.
How Centrifugal Pumps Work
Centrifugal pumps operate by imparting velocity to fluid and converting that energy into flow.
Key Components:
Impeller: The rotating element that transfers energy from the motor to the fluid, increasing pressure and flow.
Volute (Casing): A spiral-shaped casing that collects fluid and directs it to the pump's discharge, converting velocity into pressure.
Motor: Powers the impeller's rotation.
Working Principle:
The impeller spins at high speed, pulling fluid into its center (the eye) and expelling it radially outward due to centrifugal force. This creates a pressure differential: low pressure at the suction inlet and high pressure at the discharge outlet, resulting in a steady flow.
Types of Centrifugal Pumps
Centrifugal pumps are classified by design and application:
Overhung Impeller Pumps:
The impeller is mounted on a shaft cantilevered from the casing.
Common types include end-suction and inline pumps.
Between-the-Bearings Pumps:
Impellers are positioned between bearings for added stability under high pressures.
Split case designs allow for easy maintenance.
Vertically Suspended Pumps:
The impeller is mounted on a vertical shaft, often used in deep well or sump applications.
Regenerative Turbine Pumps:
Employ side channel vanes for low flow, high head operations.
Circulator Pumps:
Single-stage pumps for circulating water in hydronic heating, cooling, or hot water systems.
Selecting the Right Centrifugal Pump
Choosing the right pump depends on understanding the specific needs of your system:
Flow and Pressure Requirements: Match pump capabilities with the system's operational demands.
Fluid Properties: Consider viscosity, temperature, and chemical compatibility.
System Design: Account for piping layout, head loss, and maintenance accessibility.
Conclusion
Radial (centrifugal) pumps are a reliable and efficient choice for diverse fluid transport needs. Their adaptability and straightforward design make them a go-to option for consistent flow and moderate pressure requirements.
At Bobcat Industrial Air Services in Nashville, TN, we specialize in helping businesses select, install, and maintain centrifugal pumps tailored to their specific applications. Contact us today to learn how we can enhance the efficiency and reliability of your fluid systems.
Mastering the System Curve: Optimizing Pump Systems for Maximum Efficiency
Centrifugal pumps are indispensable across industries like water treatment, industrial processes, and oil and gas. These systems depend on precision and efficiency, and understanding the system curve is vital for achieving optimal performance. At Bobcat Industrial Air Services in Nashville, TN, we emphasize the importance of leveraging the system curve to enhance pump efficiency, minimize energy costs, and maintain system longevity.
What is the System Curve?
The system curve represents the relationship between flow rate and total head (TH)—the pressure a pump must overcome to move fluid through a system. Unlike a pump curve, which describes a pump’s capacity, the system curve highlights the total resistance the system presents due to:
Static Head: The vertical distance water needs to be lifted, requiring more energy as the height increases.
Friction Head: The energy lost to resistance within pipes, fittings, valves, and other system components.
For open systems, such as residential water piping, the system curve begins at the static head and increases as flow rises due to additional friction losses. Closed systems, like heating and cooling loops, only account for friction head since there’s no vertical movement of water.
System Curve vs. Pump Curve
While the system curve represents the head required at different flow rates, the pump curve reflects the head a pump can provide at varying flow rates. These curves intersect at the pump’s operating point, which determines whether the pump can meet system demands efficiently.
A mismatch between the system and pump curves indicates that the pump is not suitable for the application. Selecting the correct pump depends on understanding how these curves interact to maintain operational balance.
Factors Affecting the System Curve
The system curve is dynamic and can change over time due to system modifications or aging infrastructure:
Pipe Characteristics: Smaller diameters, longer lengths, and surface roughness increase friction losses.
Fittings and Valves: Additional components, such as elbows or flow meters, contribute to resistance.
Aging Systems: Corrosion, scaling, and oxidation can raise friction losses over time, altering the system’s requirements.
Optimizing Pump Performance Using the System Curve
Matching the system curve with the pump curve is critical for efficiency and reliability. Key strategies include:
Adjusting Pump Speed and Impeller Size
Variable speed drives (VFDs) allow pumps to adjust dynamically to system demands, reducing energy consumption and wear. Impeller size adjustments can also shift the pump curve closer to the system’s needs. For instance, a smaller impeller may better align with the Best Efficiency Point (BEP) on the system curve, improving overall performance.
Minimizing Friction Losses
Design choices like smoother piping materials, increased pipe diameters, and shorter pipe runs can significantly reduce resistance. Optimizing the system layout further ensures efficiency.
Routine Maintenance
Regular inspections help identify and address issues like scaling, corrosion, or worn components that increase friction losses, keeping the system curve stable over time.
Why System Curves Matter
Understanding and utilizing the system curve ensures that pumps operate efficiently, reduce energy costs, and maintain a long service life. By carefully designing systems and selecting pumps that align with the system curve, you can avoid inefficiencies and prevent costly downtime.
At Bobcat Industrial Air Services in Nashville, TN, we specialize in pump system optimization and maintenance. Our team helps businesses analyze system curves to select the right pumps, adjust configurations, and keep operations running smoothly. Contact us today to learn how we can improve your pump system’s efficiency and reliability.
Maximizing Pump Performance: Understanding Net Positive Suction Head (NPSH)
In the world of centrifugal pumps, Net Positive Suction Head (NPSH) plays a pivotal role in ensuring efficiency, preventing cavitation, and extending the lifespan of equipment. At Bobcat Industrial Air Services in Nashville, TN, we emphasize the importance of understanding NPSH to keep your pumps running smoothly and your systems operating at peak performance.
What is Net Positive Suction Head (NPSH)?
NPSH refers to the pressure available at the suction side of a pump to prevent the liquid from vaporizing. It is a balance between the system's available pressure and the pump's required pressure to avoid issues like cavitation.
Two Forms of NPSH:
NPSH Available (NPSHA): A property of the system, NPSHA is the pressure delivered to the pump suction. Factors influencing NPSHA include:
Surface pressure on the supply tank
Elevation difference between the water source and pump centerline
Friction losses in the suction piping
Velocity head and vapor pressure of the fluid
NPSH Required (NPSHR): A property of the pump, NPSHR is the minimum pressure needed at the pump suction to avoid cavitation. It is determined by factors such as impeller design and rotational speed and is specified by the manufacturer.
Why is NPSH Important?
NPSH ensures that the fluid entering the pump remains in its liquid state, avoiding cavitation—a phenomenon where vapor bubbles form and collapse violently within the pump. Cavitation can damage impellers, casings, and other components, reducing efficiency and causing premature failure.
To avoid cavitation, NPSHA must always exceed NPSHR. Selecting a pump where NPSHR exceeds NPSHA will lead to inefficiencies, increased maintenance, and reduced pump life.
Common Issues Caused by Inadequate NPSH
Reduced Capacity: The pump struggles to move fluid effectively.
Vibration and Noise: Cavitation disrupts smooth operation, leading to instability.
Component Erosion: Repeated cavitation erodes impellers and other parts, increasing maintenance costs and reducing lifespan.
Factors Influencing NPSH
System Design and Friction Losses:
Static Head: A higher water level above the pump’s centerline increases NPSHA, while a lower water source reduces it, causing the pump to work harder.
Piping Diameter: Larger diameters reduce friction losses and increase NPSHA, while smaller diameters do the opposite.
Suction Piping Configuration: Excessive valves, elbows, and fittings increase friction losses, lowering NPSHA.
Pump Speed:
Higher Flow Rates: Increased pump speed raises flow rates, causing greater pressure drops in the suction piping and reducing NPSHA.
Increased NPSHR: As pump speed rises, the pump requires more pressure to operate effectively, further increasing NPSHR.
Altitude:
At higher altitudes, atmospheric pressure decreases, lowering water’s boiling point and vapor pressure. This reduces NPSHA and increases the likelihood of cavitation. For example, water boils at 212°F at sea level but at a much lower temperature at higher altitudes like Denver, CO, where atmospheric pressure is significantly reduced.
Best Practices to Maintain Proper NPSH
System Design Optimization: Ensure minimal friction losses by using appropriately sized piping and avoiding excessive fittings.
Proper Pump Selection: Choose a pump with an NPSHR that aligns with the system’s NPSHA, ensuring a sufficient margin.
Regular Maintenance: Monitor system performance, including flow rates and pressure, to identify and address issues early.
Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs): Use VFDs to control pump speed dynamically, maintaining optimal flow rates and preventing excessive pressure drops.
Understanding the NPSH Balance
Think of NPSHA and NPSHR as a pump’s income and expenses. To maintain a stable operation, the available pressure (NPSHA) must always exceed the required pressure (NPSHR). By staying within this balance, you can prevent cavitation, improve pump efficiency, and extend the lifespan of your equipment.
At Bobcat Industrial Air Services in Nashville, TN, we specialize in pump system design, selection, and maintenance to help businesses avoid common pitfalls related to NPSH. Contact us today to learn how we can optimize your system and keep your pumps performing at their best.
Avoiding Pump Performance Pitfalls: Staying Within the Best Efficiency Point (BEP)
The Best Efficiency Point (BEP) is a critical concept in centrifugal pump performance. It represents the flow rate at which a pump operates most efficiently, with minimal energy loss and mechanical wear. Operating too far to the left or right of BEP can cause inefficiencies, increased maintenance costs, and long-term damage to pump components. At Bobcat Industrial Air Services in Nashville, TN, we work with businesses to ensure their pumps operate within optimal ranges, maximizing performance and minimizing downtime.
Understanding the BEP on Performance Curves
The BEP marks the sweet spot on a pump performance curve, where the balance between flow rate, head, and energy consumption is optimized. At this point, the impeller experiences minimal radial force, leading to smooth operation with low vibration and noise. Staying near the BEP reduces energy costs, enhances reliability, and extends the lifespan of the pump.
What Happens When Pumps Operate Beyond BEP?
While pumps are designed to handle a range of flow rates and pressures, operating too far from the BEP—either to the right (higher flow) or left (lower flow)—can cause significant challenges.
Operating Too Far Right of BEP
When pumps run at higher-than-optimal flow rates, they can experience:
High Velocity and Turbulence: Increased wear on the impeller and casing due to excessive water movement.
Motor Overload: Higher power consumption can lead to overheating and motor damage.
Cavitation: At higher flow rates, the Net Positive Suction Head Required (NPSHr) increases, potentially exceeding the Net Positive Suction Head Available (NPSHa). This can cause cavitation, leading to impeller erosion and reduced efficiency.
Reduced Lifespan: Consistent high-flow operation shortens component life due to wear and strain.
Operating Too Far Left of BEP
Low-flow operation can also have severe consequences:
Internal Circulation and Erosion: Recirculated water may carry small solids or abrasives that damage the impeller and casing.
Increased Vibration and Noise: Low flow rates create unbalanced water dynamics, leading to excessive vibration and potential damage to seals and bearings.
Overheating: Insufficient water movement can cause heat buildup, leading to pump failure.
Low-Flow Cavitation: Reduced pressure in the pump can cause vapor bubbles to form and collapse, damaging components.
Recognizing Deviations from BEP
Monitoring and identifying when a pump operates outside its optimal range is key to avoiding damage. Signs include:
Changes in Performance: Decreased flow rates, reduced pressure, or spikes in energy consumption.
Visual and Auditory Indicators: Unusual noise, vibration, or leaks.
Monitoring Tools: Flow meters, pressure gauges, and vibration sensors can detect deviations in real-time.
Staying Near the BEP
To maintain performance near the BEP, manufacturers and industry standards define operational ranges:
Preferred Operating Region (POR): A range within 70-120% of BEP, offering reliable performance and minimal wear.
Allowable Operating Region (AOR): A broader range determined by manufacturers for continuous operation without significant degradation, though outside this range, efficiency and reliability drop significantly.
Strategies to Optimize Pump Operation
Proper Sizing and Selection: Choose pumps designed for specific applications that align with expected flow and pressure requirements.
Regular Maintenance: Inspect and monitor pump performance regularly to catch issues early.
Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs): Use VFDs to adjust pump speed dynamically based on system demands.
System Design Optimization: Minimize resistance by optimizing pipe sizes, valve placement, and other system components.
Conclusion
Operating a pump too far to the left or right of its BEP can cause inefficiencies, higher operational costs, and premature wear. By understanding these risks and implementing strategies to maintain operation near the BEP, you can ensure maximum efficiency and longevity for your equipment.
At Bobcat Industrial Air Services in Nashville, TN, we specialize in pump selection, system optimization, and maintenance to keep your equipment running at peak performance. Contact us today to learn how we can help you extend the life of your pumps and improve your overall system efficiency.
Understanding Total Head: The Key to Optimal Pump Performance
Total Head (TH) is a crucial factor in the design and operation of efficient pumping systems. Representing the total energy required to move water through a system, TH is essential for selecting the right pump, optimizing operations, and maintaining energy efficiency. At Bobcat Industrial Air Services in Nashville, TN, we recognize the importance of Total Head in ensuring reliable and cost-effective pumping solutions for a variety of applications.
What is Total Head?
Total Head, formerly known as Total Dynamic Head, is a measurement of the energy a pump must exert to overcome system resistance and deliver water from one point to another. This resistance includes two main components:
Static Head (Elevation Loss): The vertical distance water needs to be lifted.
Friction Head (Friction Loss): The energy lost as water flows through pipes, fittings, and other system components.
By accurately calculating Total Head, engineers can design efficient systems that minimize energy waste and extend pump lifespan.
The Impact of Inaccurate Total Head Calculations
Using a pump with incorrect Total Head specifications can lead to:
Reduced Flow Rates: Insufficient energy causes slower water delivery.
Overheating and Damage: The pump overworks to compensate for resistance, leading to wear and tear.
Inefficient Operation: Excessive energy consumption increases costs.
Cavitation: Insufficient suction pressure causes vapor bubbles to form and collapse, damaging pump components.
Proper Total Head calculations ensure smooth operation and prevent costly issues.
Components of Total Head
Static Head (Elevation Loss)
Static head refers to the vertical distance water must travel against gravity. As height increases, more energy is required to maintain flow. For example, a pump servicing a tall building must overcome significant elevation losses to deliver water effectively.
Pressure in the pump industry is often expressed in “feet of head” rather than pounds per square inch (psi), where 1 psi = 2.31 feet of head.
Friction Head (Friction Loss)
Friction head accounts for the resistance water encounters as it flows through a system. Factors that contribute to friction loss include:
Pipe Diameter: Smaller pipes create more resistance.
Surface Roughness: Even smooth materials like PVC and copper exhibit minor roughness that impacts flow.
Length of Pipe: Longer pipes result in greater friction losses.
Fittings and Valves: Elbows, joints, and valves add resistance, equivalent to additional pipe length.
For instance, a 2-inch pipe with a 70-gallon-per-minute flow experiences more friction loss over 110 feet compared to 50 feet. Similarly, a 90-degree elbow can add friction loss equivalent to 5.5 feet of straight pipe.
Calculating Total Head
To determine the Total Head required for a system, combine static head and friction head:
Total Head (TH) = Static Head + Friction Head
By adding these components, you can size a pump accurately to meet system requirements. For example, a pump delivering 125 feet of Total Head is ideal for a 100-foot-tall building with 210 gallons per minute (gpm) flow through 3-inch copper piping.
Designing an Efficient System
At Bobcat Industrial Air Services in Nashville, TN, we emphasize the importance of system design in minimizing friction loss, installation costs, and operational expenses. By considering factors such as pipe materials, diameter, and layout, we help businesses create systems that operate efficiently and effectively.
Partner with Bobcat Industrial Air Services
Whether you're designing a new system or troubleshooting an existing one, understanding Total Head is essential for achieving reliable performance and energy efficiency. Contact Bobcat Industrial Air Services in Nashville, TN, for expert guidance on pump selection, system design, and maintenance to keep your operations running smoothly.
Pressure Perfect: Selecting the Right Multi-Pump Pressure Booster System
Maintaining consistent water pressure is essential for the smooth operation of water systems in multi-story buildings, industrial facilities, agricultural applications, and municipal infrastructures. Insufficient pressure can lead to interrupted water flow, diminished system performance, and user dissatisfaction. Pressure booster systems provide a reliable solution by ensuring adequate water pressure across various applications.
At Bobcat Industrial Air Services in Nashville, TN, we understand the importance of selecting the right pressure booster system for your specific needs. Here’s an in-depth guide to how these systems work, their applications, and the factors to consider when choosing a multi-pump pressure booster system.
What is a Pressure Booster System?
A pressure booster system is designed to enhance or maintain water pressure, ensuring consistent flow to multiple delivery points. Whether it’s residential apartments, high-rise office buildings, or industrial facilities, these systems address fluctuations or inadequacies in water pressure to keep operations running smoothly.
For high-rise buildings, booster systems efficiently distribute water across floors, ensuring comfort and reliability for tenants and employees. Tailored to meet specific requirements, these systems maintain optimal water pressure for various fixtures, enhancing overall system performance.
Applications of Pressure Booster Systems
Pressure booster systems play a critical role in various settings:
Residential: Ensure sufficient water pressure for households, including simultaneous use of multiple fixtures and appliances in apartment buildings or single-family homes.
Commercial: Provide reliable water pressure for hotels, office buildings, and lawn irrigation systems.
Municipal: Support water treatment and distribution systems by maintaining consistent pressure levels.
Industrial: Power high-pressure water processes, such as cooling, cutting, or cleaning.
Agricultural: Supply irrigation systems and distribute water efficiently across farms and livestock facilities.
How Multi-Pump Pressure Booster Systems Work
As water travels through pipes, it loses pressure due to elevation changes and friction. Single pumps often struggle to maintain sufficient pressure, especially in systems with high demand or significant elevation differences. Multi-pump pressure booster systems address these challenges by working in parallel to optimize flow and pressure.
Variable Demand Management: Equipped with Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs), these systems activate additional pumps only during peak demand periods, conserving energy during lower usage times.
Load Sharing: Pumps in parallel configurations share workloads, ensuring consistent pressure while reducing strain on individual pumps.
Adaptability: These systems adjust seamlessly to fluctuating flow rates, maintaining efficiency and reducing operational costs.
Key Factors When Sizing a Pressure Booster System
Choosing the correct pressure booster system requires a comprehensive evaluation of your building’s needs:
Total Head (TH): Consider both elevation losses (height from the supply line to the highest fixture) and friction losses (pipe size, age, material, and system obstructions).
Gallons Per Minute (GPM): Estimate water demand using fixture counts and detailed plumbing code charts to calculate the required flow rate.
Incoming Pressure: Evaluate municipal water supply pressure and calculate the additional boost needed to meet building requirements.
Type of Pump: Select single-stage or multi-stage pumps based on pressure and flow needs. Compact vertical pumps can save space, while multi-stage systems handle higher TH requirements.
Number of Pumps: Choose between simplex (single pump) or multi-pump configurations, incorporating redundancy for critical systems to ensure reliability.
Automation: Consider advanced monitoring systems with sensors and analytics to optimize performance and energy efficiency.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
When investing in a pressure booster system, avoid these common mistakes:
Undersizing or oversizing pumps, which can lead to inefficiencies or system failures.
Overlooking potential future expansion needs.
Ignoring pressure losses caused by static or friction head.
Neglecting to evaluate incoming water pressure accurately.
The Bobcat Advantage
At Bobcat Industrial Air Services in Nashville, TN, we specialize in designing and maintaining customized pressure booster systems tailored to your specific requirements. With our expertise, we help you select the most efficient and reliable solution to enhance water pressure while reducing energy and lifecycle costs.
A pressure booster system is a significant investment that pays for itself through improved performance, energy savings, and system longevity. Contact Bobcat Industrial Air Services to learn more about how we can support your building's water pressure needs.
Self-Priming Pumps vs. Centrifugal Pumps: A Comprehensive Comparison
Pumps are essential for moving fluids across industries, supporting processes in water supply, wastewater treatment, chemical processing, and more. Selecting the right type of pump is crucial, and Bobcat Industrial Air Services in Nashville, TN, offers expertise in both self-priming and centrifugal pumps to meet specific application needs. Here, we’ll explore the key distinctions between these two types, aiding decision-making for various industrial requirements.
Self-Priming Pumps
Self-priming pumps eliminate the need for manual priming, making them ideal for applications with suction lifts—situations where the pump is above the liquid source. They rely on a specialized impeller design and air-water separation mechanisms, which allow them to expel air automatically and establish a consistent flow of liquid. This automatic priming feature is a valuable asset in sectors like agriculture, construction, and wastewater management, especially in locations with unreliable water sources or in operations where frequent priming isn’t feasible.
Bobcat Industrial Air Services supports clients with self-priming pump solutions for remote or challenging conditions, providing reliable performance in intermittent operations that might otherwise require constant manual intervention.
Centrifugal Pumps
Centrifugal pumps, one of the most commonly used pump types, operate by accelerating fluid outward through a rotating impeller, creating a pressure gradient that drives fluid through the pump. However, traditional centrifugal pumps require manual or external priming if they are not positioned below the fluid source, as they rely on gravity to fill the pump and suction lines. Centrifugal pumps are available in various types, such as single-stage, multi-stage, and split-case configurations, making them versatile for applications in water supply, HVAC systems, and large-scale industrial fluid transport.
At Bobcat Industrial Air Services, centrifugal pumps are customized to meet the demands of industries needing efficient, high-capacity fluid movement, such as chemical processing and cooling systems in power plants.
Factors Influencing Pump Choice
Selecting the ideal pump requires considering multiple factors:
Fluid Properties: The fluid’s viscosity and corrosiveness affect material selection. For instance, abrasive or corrosive fluids may require robust materials, impacting pump longevity and reliability.
Flow Rate and Pressure: Required flow rate and pressure determine the pump’s size and capacity, ensuring it meets the operational demands.
System Layout and Constraints: Space limitations and installation constraints influence pump configuration.
Cost and Efficiency: Evaluating initial investment, long-term operational costs, and energy efficiency helps balance budget considerations with sustainable performance.
Bobcat Industrial Air Services provides tailored solutions, taking these factors into account to ensure clients receive the most suitable pump for their applications.
Case Studies and Applications
Self-priming pumps are frequently used in agricultural applications where water needs to be lifted from wells or other sources. For example, in remote or arid areas, self-priming pumps provide a dependable water source without the need for constant manual priming. Conversely, centrifugal pumps are often employed in large-scale operations, such as cooling water circulation in power plants, where they efficiently handle high fluid volumes necessary for heat dissipation.
Emerging Trends in Pump Technology
The future of pump technology promises advancements in both self-priming and centrifugal pumps. For self-priming pumps, developments are underway to enhance air-handling mechanisms, improving performance under challenging conditions. Centrifugal pumps are expected to benefit from new impeller designs and control systems that increase efficiency and adapt to varying operational demands. Additionally, automation and IoT integration are expected to make pumps more responsive, reducing downtime and operational costs.
Conclusion
When choosing between self-priming and centrifugal pumps, it’s essential to evaluate the specific requirements of the application. Self-priming pumps excel in situations where automatic priming is needed, such as in suction lift applications and intermittent operations. On the other hand, centrifugal pumps remain a versatile choice for continuous fluid movement, handling high-volume tasks with ease. By understanding the differences between these pump types and consulting with experts like Bobcat Industrial Air Services in Nashville, TN, industries can optimize pump performance, reduce costs, and ensure reliable fluid movement across various settings.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main advantage of self-priming pumps over traditional centrifugal pumps?
Self-priming pumps can automatically handle air, eliminating the need for manual priming. This is especially useful in applications where the pump is situated above the fluid source.Are self-priming pumps complex to install and maintain?
Both self-priming and centrifugal pumps have moderate installation and maintenance requirements. Self-priming pumps may need slightly more attention to ensure their air-handling mechanisms are functioning optimally.In which industries are self-priming pumps commonly used?
Self-priming pumps are prevalent in agriculture, construction, municipal water supply, and wastewater management, especially where automatic priming is essential.Can centrifugal pumps handle suction lifts?
Centrifugal pumps can manage suction lifts but require manual or external priming to address air entrainment, making self-priming pumps a more efficient solution in these cases.Are there recent advancements in pump technology affecting self-priming and centrifugal pumps?
Yes, advancements in impeller design, materials, and control systems are improving pump efficiency and adaptability. Self-priming pumps are seeing improved air-handling capabilities, while centrifugal pumps are benefiting from automation and enhanced efficiency.
With expert guidance from Bobcat Industrial Air Services, businesses can confidently select the pump that best suits their operational needs, balancing performance with practicality and efficiency.
Selecting the Right Pump for Your Specific Application: A Comprehensive Guide
Selecting the appropriate pump for an application is crucial across industries, directly impacting efficiency, safety, and operational success. Bobcat Industrial Air Services in Nashville, TN, offers extensive expertise in pump selection and maintenance, ensuring clients achieve optimal results. This guide provides insights into the fundamentals of pump technology, factors for evaluating applications, and practical steps to make the best pump choice.
Understanding Pump Basics
Pumps transport fluids efficiently and accurately, playing an essential role in processes ranging from water circulation to hazardous chemical transfer.
Definition and Purpose of a Pump
A pump moves fluids by imparting energy to enable fluid displacement or compression, serving various needs from heating systems to industrial fluid transfer.
Different Types of Pumps
Bobcat Industrial Air Services offers a range of pump types, each tailored for specific industry applications:
Centrifugal Pumps: Utilizing an impeller to create centrifugal force, these pumps excel in high-flow, low-pressure applications, such as HVAC systems and wastewater treatment. They are ideal for continuous, high-volume fluid transport.
Case Study: In a commercial building, centrifugal pumps circulate water efficiently through the HVAC system, exemplifying their role in high-flow applications.
Positive Displacement Pumps: Providing a consistent flow, these pumps handle high-viscosity fluids well and are perfect for applications like oil transfer, food processing, and chemical production.
Case Study: Positive displacement pumps in an oil refinery enable reliable crude oil transfer, a high-viscosity process essential to refinery operations.
Specialized Pumps: Diaphragm and peristaltic pumps are ideal for unique, precision applications. Diaphragm pumps are valuable in chemical dosing for water treatment, while peristaltic pumps are used in sensitive industries like pharmaceuticals and food.
Assessing Application Requirements
Selecting a pump involves analyzing the specific demands of each application.
Fluid Properties: The fluid’s viscosity, temperature, and corrosiveness influence pump compatibility.
Viscosity: High-viscosity fluids require pumps like positive displacement pumps.
Temperature: Temperature resilience is critical for longevity, requiring compatible materials.
Corrosiveness: For corrosive fluids, select materials that resist chemical degradation.
Flow Rate and Pressure Requirements: Identifying these parameters ensures the pump aligns with operational needs.
Flow Rate: Determines the fluid volume the pump can manage.
Pressure: Indicates the force needed for fluid propulsion.
System Constraints: Consider space limitations, environmental factors, and budget constraints to ensure the pump fits the setting.
Matching Pump Types to Applications
Matching the right pump to specific needs maximizes efficiency. For example:
Centrifugal Pumps: Suitable for high-flow, low-pressure applications, such as water circulation in large facilities.
Positive Displacement Pumps: Ideal for high-viscosity and high-pressure applications, ensuring steady fluid transfer regardless of system variations.
Bobcat Industrial Air Services provides tailored recommendations to align pump choice with precise industry needs, optimizing performance and cost-efficiency.
Evaluating Manufacturer and Supplier
Choosing a reliable supplier is critical for receiving a quality pump that meets application requirements.
Reputation and Track Record: Bobcat Industrial Air Services has a trusted reputation, ensuring clients receive dependable products and comprehensive support.
Support and Service Availability: Look for manufacturers offering extensive technical support, maintenance, and parts availability.
Customization Options: Specific applications may require custom features; inquire about modifications to ensure the pump meets unique specifications.
Sizing and Installation
Proper sizing and installation are vital for efficient operation.
Sizing the Pump: Analyze pump curves and system curves to determine the optimal flow rate and pressure, ensuring the pump meets the application’s needs.
Installation Best Practices: Select appropriate installation locations and follow best practices for mounting, alignment, and safety.
Testing and Commissioning
Before full operation, conduct pre-operational checks, start-up procedures, and initial monitoring.
Pre-operational Checks: Inspect all components for any signs of damage, leaks, or loose connections.
Monitoring Initial Operation: Track performance metrics like flow rate and pressure during initial operation to confirm correct function.
Troubleshooting and Maintenance
Bobcat Industrial Air Services advises on common issues and maintenance practices to sustain pump performance:
Common Problems: Cavitation, seal leakage, and vibration can impact performance, requiring systematic troubleshooting.
Preventative Maintenance: Routine inspection, lubrication, and wear-part replacement prolongs pump life.
Case Studies and Real-World Applications
Water Treatment Plant Example: A diaphragm pump in a water treatment facility accurately doses chemicals, maintaining safe pH levels.
Petrochemical Refinery Example: Positive displacement pumps transfer crude oil reliably, supporting continuous production.
Future Trends in Pump Technology
Pump advancements include smart sensors, energy-efficient designs, and sustainable materials, promising enhanced performance, lower environmental impact, and cost savings.
Conclusion
Selecting the right pump impacts operational success and efficiency across industries. By understanding pump types, application requirements, and installation best practices, businesses can achieve reliable fluid handling tailored to their needs. Bobcat Industrial Air Services in Nashville, TN, provides expertise and solutions, helping industries meet unique demands while staying ahead of trends in pump technology. With informed selection and maintenance, businesses can rely on pump systems to drive productivity and maintain safety in critical applications.
Installation and Maintenance of End Suction Pumps: A Comprehensive Guide
End suction pumps are crucial in industries such as water supply, HVAC, wastewater management, and agriculture. Proper installation and maintenance ensure reliable performance, reduced downtime, and extended pump life. Bobcat Industrial Air Services in Nashville, TN, offers expertise in end suction pump solutions, supporting businesses with comprehensive installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting services. This guide explores the essentials of working with end suction pumps, covering safety measures, setup, maintenance, and diagnostics.
Understanding End Suction Pumps
End suction pumps, also called ES pumps, are centrifugal pumps featuring a single inlet and outlet. Key components include:
Impeller: Drives fluid flow, impacting pump performance.
Casing: Encloses the impeller, directing fluid.
Shaft: Connects the motor to the impeller, requiring alignment for longevity.
Motor: Powers the impeller, essential for overall pump function.
Bobcat Industrial Air Services helps clients select and install the right pump type for specific needs, including close-coupled, base-mounted, and vertical inline configurations, each suited for various applications.
Common Applications
End suction pumps serve numerous industries:
Water Supply: For municipal water distribution and well pumping.
Heating and Cooling: Essential for HVAC systems and boiler feeds.
Wastewater Management: Used in sewage treatment and effluent pumping.
Industrial Processes: Supports chemical and food processing.
Agriculture: Used for irrigation and livestock operations.
Safety Precautions
Ensuring safety is paramount during installation and maintenance. Recommended precautions include:
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Use goggles, gloves, and appropriate footwear.
Lockout/Tagout (LOTO): Prevent accidental startup during maintenance.
Electrical Safety: Disconnect power before maintenance and inspect wiring.
Handling Hazardous Materials: If handling chemicals, follow safety protocols and maintain proper ventilation.
Bobcat Industrial Air Services emphasizes the importance of safety, training teams on best practices to minimize risks.
Installation Procedures
Proper installation ensures pump efficiency and longevity:
Site Preparation: Select a location for accessibility and minimal environmental impact. Ensure a stable foundation.
Pump Assembly: Align and connect the motor and pump following manufacturer guidelines. Precise alignment reduces wear and prolongs pump life.
Piping and Connections: Use appropriately sized suction and discharge pipes to reduce friction loss. Install check and isolation valves to control flow.
Electrical Connections: Follow the motor’s wiring diagram, and ensure the setup includes circuit breakers and overload protection.
Commissioning and Testing: Prime the pump, vent air, and test flow rate, pressure, and vibration levels.
Bobcat Industrial Air Services supports each installation phase, ensuring precision and adherence to best practices.
Maintenance Procedures
Regular maintenance is essential to prevent issues and optimize performance:
Regular Inspection: Visual checks for leaks, corrosion, and worn parts.
Lubrication: Follow lubrication schedules for bearings and seals.
Seal and Gasket Maintenance: Regularly inspect and replace worn seals and gaskets to prevent leaks.
Impeller and Casing Inspection: Clean and maintain these parts to avoid performance loss.
Bearing and Shaft Alignment: Periodic alignment checks maintain smooth operation.
Troubleshooting
Bobcat Industrial Air Services provides diagnostic tools and expertise for common issues:
Cavitation: Caused by low-pressure zones, cavitation damages the pump over time. Solutions include adjusting flow and checking system design.
Low Flow or Pressure: Caused by blockages, misalignment, or worn impellers.
Noise and Vibration: Addressed by checking alignment and inspecting bearings.
Leakage: Promptly fix leaks to avoid environmental and equipment damage.
Preventive Maintenance and Environmental Considerations
Implementing a preventive maintenance schedule is essential. Bobcat Industrial Air Services assists with:
Predictive Maintenance: Using vibration analysis and oil analysis to anticipate issues.
Spare Parts Management: Stocking essential parts to avoid delays.
Energy Efficiency: Reducing costs with energy-efficient pumps and sustainable practices, including variable frequency drives (VFDs).
Conclusion
Proper installation and maintenance of end suction pumps are crucial for efficient, uninterrupted operations. Bobcat Industrial Air Services in Nashville, TN, offers a comprehensive range of services, from pump selection to installation, maintenance, and troubleshooting. By following these best practices, businesses can maximize pump performance and longevity, ensuring a dependable fluid management system tailored to their specific needs.
Choosing the Right Pump: End Suction vs. Horizontal Split-Case Pumps
Centrifugal pumps are vital across many industries, aiding in fluid movement for HVAC, water supply, irrigation, and more. Selecting the right pump type is essential to ensure operational efficiency and performance. Bobcat Industrial Air Services in Nashville, TN, provides expert guidance on pump selection, installation, and maintenance. This guide compares two commonly used centrifugal pumps: end suction and horizontal split-case, helping you choose the best option for your application.
End Suction Pumps
Definition and Basic Design Features
End suction pumps have a single-stage impeller, with an inlet at one end and a discharge outlet perpendicular to the pump shaft. Their compact design makes them easy to install and maintain, making them popular in various settings.
Advantages
Compact and Space-saving: Ideal for limited-space installations, such as HVAC systems and building water supplies.
Simple Installation and Maintenance: With fewer components, end suction pumps are relatively straightforward to install and maintain.
Best for Low to Medium Flow Rates and Head Pressures: Suitable for applications where moderate flow and pressure are required.
Limitations
Not Ideal for High-Pressure Applications: Split-case pumps are more suitable for high-pressure scenarios.
Risk of Cavitation at High Flow Rates: End suction pumps may be prone to cavitation if flow rates exceed recommended levels.
Efficiency Drops at Varying Flow Rates: They are less efficient in applications with fluctuating demands.
Horizontal Split-Case Pumps
Definition and Basic Design Features
Horizontal split-case pumps feature a two-part casing split along the horizontal plane, housing a double-suction impeller. This design provides excellent efficiency, stability, and reliability.
Advantages
High Efficiency and Reliability: Ideal for high flow and head pressures, split-case pumps are known for their reliable performance.
Effective for High Flow and Pressure Applications: These pumps are well-suited for industries requiring large fluid volumes against significant resistance.
Reduced Cavitation Risk: The double-suction impeller minimizes cavitation, ensuring consistent flow.
Limitations
Larger Space Requirement: Split-case pumps typically require a larger footprint, limiting their use in compact areas.
More Complex Installation and Maintenance: With more components, installation and maintenance may take more time and expertise.
Higher Initial Cost: Split-case pumps generally have a higher initial investment than end suction pumps.
Application Considerations
Industry Examples
End Suction Pumps: Common in HVAC systems, building water supplies, and irrigation due to their compact size and suitability for moderate flow rates.
Horizontal Split-Case Pumps: Used in municipal water supplies, industrial processes, and power generation, where high flow rates and pressures are necessary.
Bobcat Industrial Air Services advises on industry-specific applications, helping clients make informed choices based on unique requirements.
Performance and Efficiency
Efficiency Comparison
Split-case pumps generally perform more efficiently in high-flow and high-pressure conditions than end suction pumps. While split-case pumps may have higher upfront costs, they provide energy savings in the long run, especially in high-demand applications.
Energy and Operating Costs
End suction pumps are cost-effective in low-to-medium flow systems, while split-case pumps reduce long-term costs in high-demand settings due to their efficiency.
Considerations for Variable Flow Applications
Split-case pumps handle varying flow rates better, making them more suitable for systems with fluctuating demands. End suction pumps, however, may experience reduced efficiency with changes in flow rate.
Maintenance and Serviceability
Maintenance Requirements
End suction pumps have simpler designs, resulting in easier maintenance. Split-case pumps, with their additional components, may require specialized expertise for servicing.
Downtime Considerations
Downtime is crucial in continuous operations. End suction pumps offer quicker maintenance, while split-case pumps may need more time but provide durable, stable performance in high-demand systems.
Cost Analysis
Initial Capital Costs and Lifecycle Cost
Split-case pumps generally require a higher initial investment. However, considering the lifecycle costs—including maintenance and energy savings—they can prove cost-effective for long-term applications. Bobcat Industrial Air Services offers consultations to determine the best value option for specific applications.
Environmental Considerations
Energy Efficiency and Impact
Efficient pumps reduce operational costs and environmental impact. Bobcat Industrial Air Services assists clients in identifying energy-efficient options for sustainable operations. Split-case pumps often qualify for rebates and incentives due to their efficiency in high-demand applications.
Conclusion
Choosing between end suction and horizontal split-case pumps requires a thorough assessment of system needs. End suction pumps offer simplicity and are suited for low to medium flow applications, while split-case pumps excel in high-flow, high-pressure settings. By consulting with Bobcat Industrial Air Services in Nashville, TN, businesses can ensure they select the pump that best meets their application requirements, balancing space, cost, and long-term efficiency.
Exploring the Advantages and Disadvantages of Self-Priming Pumps
Self-priming pumps have become essential in modern fluid management systems, offering unique advantages while presenting some challenges. This guide, with insights from Bobcat Industrial Air Services in Nashville, TN, explores the pros and cons of self-priming pumps, examining their real-world applications and future potential.
Advantages of Self-Priming Pumps
A. Elimination of Manual Priming
No More Manual Priming: Conventional pumps often require manual priming, which is time-consuming and labor-intensive. Self-priming pumps automate this process, allowing them to start fluid flow without needing manual intervention.
Automated Priming Benefits: Self-priming pumps are designed to evacuate air and gases from the suction line automatically, enabling instant and efficient operation, minimizing setup time, and eliminating the need for continuous supervision.
B. Handling of Air and Gases
Challenges in Traditional Pumps: Conventional pumps struggle with air-water mixtures, leading to cavitation, efficiency loss, and potential pump damage.
Self-Priming Pumps’ Adaptability: These pumps are engineered to handle air and gas mixtures efficiently, maintaining consistent fluid flow without interruptions from air entrapment. This capability is particularly beneficial for industries dealing with varying fluid conditions.
C. Time and Labor Savings
Reduced Priming Time: Self-priming pumps start immediately, saving valuable time in comparison to traditional pumps that require lengthy priming.
Lower Personnel Demand: These pumps require minimal manual intervention, freeing personnel to focus on other tasks—a key benefit in industries with limited workforce availability.
D. Versatility and Ease of Installation
Adaptability Across Fluid Types: Self-priming pumps are versatile, handling various fluids with ease, making them suitable for multiple industries, including agriculture and construction.
Simplified Installation: With no need for additional priming mechanisms, self-priming pumps reduce infrastructure requirements, allowing faster and more straightforward installation.
Disadvantages of Self-Priming Pumps
A. Initial Cost
Higher Upfront Investment: Due to their advanced design, self-priming pumps typically cost more initially than standard pumps.
Long-Term Cost Benefits: Despite the upfront cost, the savings in time, labor, and efficiency often justify the investment, especially for businesses prioritizing operational efficiency.
B. Complex Design and Maintenance
Intricate Mechanisms: While their complexity enables self-priming capabilities, it also requires regular maintenance and specialized knowledge.
Skilled Maintenance Needed: Ensuring optimal performance demands technicians familiar with self-priming pump technology. Bobcat Industrial Air Services offers maintenance and repair services to manage these intricate systems effectively.
C. Performance Limitations at High Suction Lifts
Efficiency Reduction at High Lifts: Self-priming pumps may become less efficient as suction lift heights increase.
Best Used in Moderate Lift Applications: While versatile, self-priming pumps are generally more efficient at lower to moderate suction lifts, making them suitable for specific applications.
D. Sensitivity to Particle Size and Viscosity
Particle Size Challenges: High particle content in fluids can lead to clogs, reducing pump efficiency.
Viscosity Concerns: Self-priming pumps may struggle with highly viscous fluids, which require design adjustments for smooth operation.
Applications of Self-Priming Pumps
Bobcat Industrial Air Services has implemented self-priming pump solutions across a variety of industries, enhancing productivity and reliability.
Domestic Water Supply: Self-priming pumps ensure consistent flow for residential needs, particularly in well water systems.
Construction and Dewatering: Common on construction sites, these pumps quickly remove water, preventing delays and safety hazards.
Marine Industry: In boats and ships, self-priming pumps remove unwanted water efficiently, essential for vessel safety and stability.
Agriculture and Irrigation: These pumps deliver efficient water distribution across farmlands, vital for irrigation and crop growth.
Case Studies: Real-World Implementations
Municipal Wastewater Management: Self-priming pumps have improved the reliability of wastewater pumping stations by automatically handling air entrapment and reducing downtime.
Oil and Gas Industry: In oil transfer operations, self-priming pumps have proven invaluable, mitigating air entrapment risks and enhancing safety while minimizing downtime.
Conclusion
Self-priming pumps have revolutionized fluid management, offering benefits in time savings, labor reduction, and operational versatility. Despite their higher initial cost and maintenance demands, they continue to serve vital roles across industries. With guidance from Bobcat Industrial Air Services, businesses can navigate these challenges, optimizing self-priming pumps to meet specific operational needs. As technology progresses, self-priming pumps will likely evolve further, expanding their capabilities and offering even more sophisticated solutions for fluid transport and management.
Maintenance Tips to Extend the Lifespan of Chemical Pumps
Chemical pumps are essential in industries ranging from pharmaceuticals to mining, moving hazardous and delicate substances reliably. But without proper care, they can quickly turn from assets to liabilities, with costly downtime and potential spills. Bobcat Industrial Air Services in Nashville, TN, offers comprehensive pump maintenance services to keep your operations running smoothly. This guide explores ways to maintain and extend the lifespan of chemical pumps, ensuring they remain reliable assets in your production line.
Understanding Your Chemical Pump Types
To keep your pumps in peak condition, it’s crucial to understand their unique requirements:
Centrifugal Pumps: The Whirlwind Warriors
Centrifugal pumps are ideal for high flow rates and low-viscosity fluids. They’re widely used in bulk chemical and water transfers. However, avoid using them for abrasive materials, as they’re not built for handling solids.Gear Pumps: The Clockwork Kings
Gear pumps provide precision and control, perfect for metering chemicals or transferring viscous fluids like resins. They require regular lubrication and are sensitive to high pressures.Diaphragm Pumps: The Gentle Giants
Diaphragm pumps handle abrasive fluids well and are suitable for remote locations or hazardous environments. They’re self-priming but typically operate at lower flow rates than centrifugal or gear pumps.
Bobcat Industrial Air Services assists clients in selecting the right pumps for their specific applications and provides ongoing maintenance to keep them operating efficiently.
Essential Preventative Maintenance Practices
Regular Inspections
Routine inspections help detect potential issues early. Develop a weekly inspection schedule, particularly for critical operations. Look out for:Leaks: Check seals, connections, and packing glands.
Vibration: Unusual vibrations may indicate worn bearings, misalignment, or cavitation.
Temperature: Overheating can signal internal issues; monitor temperature against baseline levels.
Fluid Compatibility and Maintenance
Ensuring that your pump matches the fluid it handles can prevent premature wear.Use the Right Pump for the Fluid: Pumps are designed for specific viscosities and abrasive levels.
Maintain Filtration Systems: Filters prevent clogs and protect internal components from contaminants.
Monitor Fluid Temperature: Overheated fluids degrade pump performance. Cooling systems can help manage fluid temperatures.
Lubrication and Sealing
Proper lubrication and sealing prevent friction, leaks, and wear.Lubrication: Follow a schedule tailored to pump type and workload, and use the recommended lubricant.
Seal Maintenance: Check for cracks, hardening, or other signs of wear. Tighten gland nuts carefully to avoid leaks without damaging the seal.
Storage and Cleaning
Proper storage and cleaning preserve pump functionality during downtime.Storage Tips: Drain and dry pumps, apply rust prevention to metal surfaces, and store in a cool, dry location.
Cleaning Routine: Flush pumps and piping regularly to remove contaminants, especially for pumps handling corrosive or abrasive fluids.
Troubleshooting Common Pump Issues
Even with diligent maintenance, issues may arise. Here are some troubleshooting tips to keep your pumps running smoothly:
Leakage Issues: Check seals and connections. Tighten fittings or replace seals as necessary.
Reduced Performance: Ensure the pump is primed correctly, filters are clean, and there are no blockages.
Excessive Noise: Vibration or unusual sounds could indicate bearing issues or cavitation, which Bobcat Industrial Air Services can address with advanced diagnostics.
Additional Resources for Pump Mastery
Manufacturer Manuals: Consult for maintenance schedules, lubrication specs, and troubleshooting guidance.
Professional Services: Bobcat Industrial Air Services provides expert maintenance, repairs, and diagnostics for chemical pumps.
Industry Resources: Organizations like the Hydraulic Institute offer technical guides, training, and best practices for pump maintenance.
With these tips, you can extend the lifespan of your chemical pumps, optimizing productivity and minimizing downtime. Bobcat Industrial Air Services is here to support your maintenance needs, keeping your pumps running smoothly as the champions of your production line.
Exploring Various Pump Types in the Food Industry: Applications & Uses
Pumps are essential in the food processing industry, facilitating the movement of liquids, semi-solids, and solids through various production stages. With strict hygiene standards and FDA regulations, selecting the right pumps is critical to ensure food safety and quality. Bobcat Industrial Air Services in Nashville, TN, specializes in providing reliable pump solutions for the food industry, helping businesses choose the right pump types for their specific needs.
I. Introduction to Pumps in the Food Industry
In the food sector, pumps must meet stringent cleanliness and safety requirements. They play an integral role in moving ingredients through processing lines without compromising quality.
II. Classification of Pumps Based on Operating Principles
A. Positive Displacement Pumps
Rotary Pumps:
Gear Pumps: Ideal for high-viscosity products like chocolate and syrups, gear pumps use rotating gears to move fluids efficiently without altering properties.
Lobe Pumps: With gentle handling for shear-sensitive products, lobe pumps are perfect for dairy and cosmetics.
Peristaltic Pumps: Designed for handling shear-sensitive and abrasive fluids, these pumps transfer fruit juices, sauces, and similar fluids with minimal contamination risk.
Reciprocating Pumps:
Piston Pumps: Known for precise flow control, piston pumps handle high-pressure applications, making them ideal for pastes and creams.
Diaphragm Pumps: These pumps transfer substances without contamination, suitable for applications requiring high product purity.
B. Dynamic Pumps
Centrifugal Pumps:
Single-stage Pumps: Common in beverage processing, single-stage centrifugal pumps are efficient for low-viscosity fluids like milk and juices.
Multi-stage Pumps: These pumps support high-pressure applications such as pasteurization, making them ideal for systems requiring a pressure boost.
Other Dynamic Pumps:
Axial Flow Pumps: Used for moving large volumes of fluids, essential in breweries and wineries.
Mixed Flow Pumps: Efficiently handle mixtures of solids and liquids in food processing, preventing clogs and maintaining flow consistency.
III. Application-specific Considerations for Food Processing
A. Pump Materials and Construction
Stainless Steel Pumps: Stainless steel is widely used in food processing for its corrosion resistance, especially in dairy and brewing.
Sanitary Pumps: Designed with hygiene in mind, sanitary pumps feature smooth surfaces to prevent bacterial growth.
Non-metallic Pumps: For food items that react with metals, non-metallic pumps made from food-grade plastics or elastomers preserve product integrity.
B. Pump Sealing and Containment
Sealing Methods: Mechanical and double seals prevent leaks, ensuring food products remain contaminant-free.
Containment Strategies: Closed-loop systems maintain product integrity by isolating food products from external contaminants.
C. Handling Viscous and Abrasive Food Products
Viscous Fluids: For thick products like sauces, lobe and peristaltic pumps are used to maintain consistency.
Abrasion-resistant Designs: Coated pump materials withstand wear from abrasive substances, reducing maintenance.
IV. Specific Types of Food Products and Corresponding Pumps
A. Liquid Foods
Dairy Products: Sanitary positive displacement pumps handle milk gently, maintaining hygiene and product quality.
Beverages: Centrifugal pumps efficiently transfer juices and concentrates.
Sauces and Dressings: Piston and peristaltic pumps handle thick sauces like ketchup without altering texture.
B. Solid Foods and Food Particles
Handling Solids in Liquids: Rotary lobe and peristaltic pumps can manage soups and chunky sauces without damaging components.
Fruits and Vegetables: Pumps that prevent clogging, like axial flow or diaphragm pumps, are ideal for whole fruits and vegetables.
Meat Processing: For handling ground meats, peristaltic and positive displacement pumps are designed for semi-solid transport.
V. Hygiene and Cleanability in Food-grade Pumps
A. Cleaning-in-place (CIP) Systems
CIP Integration: Pumps designed for CIP allow for easy cleaning of internal surfaces, reducing contamination risks.
B. Design for Sanitation
Easy Disassembly: Pumps with smooth surfaces and minimal crevices facilitate sanitation, critical for compliance with hygiene standards.
VI. Maintenance and Operational Considerations
A. Preventive Maintenance
Routine Monitoring: Regular checks and part replacements keep pumps operating reliably, minimizing downtime.
B. Efficiency and Energy Consumption
Optimizing Efficiency: Energy-efficient pumps and variable frequency drives (VFDs) can significantly reduce costs and environmental impact.
VII. Case Studies and Industry Examples
Real-world Applications: A dairy company using sanitary rotary lobe pumps can ensure milk transfer meets hygiene standards while maintaining product quality.
Challenges Faced: Processing abrasive substances can lead to pump wear; using abrasion-resistant materials helps extend pump life.
VIII. Future Trends and Innovations
A. Emerging Technologies
Innovative Designs: Self-cleaning pumps and corrosion-resistant materials enhance durability and hygiene.
B. Digitalization Impact
Smart Sensors: Real-time performance monitoring and predictive maintenance reduce breakdowns and optimize efficiency.
IX. Conclusion
Pump selection in the food industry impacts product integrity and safety. Bobcat Industrial Air Services in Nashville, TN, provides tailored solutions that meet industry standards and enhance efficiency. By choosing the right pump types, maintaining strict hygiene, and integrating advanced technologies, food processing businesses can improve product quality, meet regulatory standards, and ensure reliable operation.
Mastering Centrifugal Pump Maintenance: A Comprehensive Checklist
Centrifugal pumps are critical components in many industrial processes, facilitating fluid movement across various sectors. Regular maintenance ensures these pumps operate efficiently, last longer, and help prevent unexpected breakdowns. Bobcat Industrial Air Services in Nashville, TN, specializes in comprehensive pump maintenance solutions to keep your centrifugal systems running smoothly. This guide provides a structured checklist to help safeguard the performance and reliability of your centrifugal pumps.
Importance of Regular Maintenance
Routine maintenance of centrifugal pumps enhances their longevity, optimizes performance, and reduces operational costs. Neglecting maintenance can lead to severe pump damage and costly repairs. Bobcat Industrial Air Services emphasizes the importance of a proactive maintenance schedule to prevent potential issues.
Safety Considerations
Proactive Safety Measures:
Lockout/Tagout Procedures: Always isolate the pump from its power source before maintenance. Proper lockout/tagout procedures help prevent accidental startups.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Use safety glasses, gloves, hearing protection, and appropriate footwear for each maintenance task.
Environmental Considerations: Be aware of the pump’s operational environment, especially if it handles hazardous materials or operates in high-risk areas.
Routine Maintenance Tasks
1. Lubrication
Bearing Lubrication: Follow manufacturer guidelines for bearing lubrication, using the recommended lubricant and ensuring it’s at the correct level.
Seal Lubrication: For pumps with seals, lubricate as specified to maintain a tight, leak-free seal.
2. Alignment Checks
Regularly check pump alignment to prevent premature wear and maintain efficiency. Misalignment is a common cause of reduced pump lifespan.
3. Vibration Analysis
Monitor vibration levels periodically. Unusual vibration patterns can indicate issues such as bearing wear or misalignment.
4. Temperature Monitoring
Regularly check temperatures of key components, including bearings and motors. Elevated temperatures may suggest problems like poor lubrication or component wear.
Daily Checks
Visual Inspection
Look for leaks at all seals and joints, and check for any visibly loose or damaged parts.
Lubrication Levels
Verify lubrication points daily, and adjust according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
Motor and Coupling
Monitor motor temperature, ensuring it doesn’t overheat, and check for coupling misalignment.
Weekly Checks
Component Inspection
Inspect the impeller and casing for any wear, and monitor bearing temperatures to detect potential issues early.
Seal Condition
Check for leakage around seals to ensure integrity.
Inlet Screens
Clean or replace inlet screens to prevent blockages that can impact pump performance.
Monthly Checks
Detailed Vibration Analysis
Record and compare vibration readings with baseline levels to identify gradual changes.
Lubrication Check
Check and replenish motor bearing lubrication.
Baseplate and Foundation Inspection
Examine the baseplate for wear or signs of shifting to maintain stability.
Quarterly Checks
Alignment Verification
Confirm the pump’s alignment with the motor to prevent efficiency losses and component wear.
Wear Ring Inspection
Check wear rings for any damage and replace them if necessary.
Annual Checks
Comprehensive Disassembly and Inspection
Disassemble the pump for an in-depth inspection of all internal components, looking for wear, corrosion, or damage.
Bearing and Seal Replacement
Replace bearings and seals as part of the annual maintenance to ensure a reliable, leak-free system.
Motor Inspection
Conduct a full motor inspection, including electrical connections and performance testing.
Troubleshooting and Common Issues
Cavitation: Cavitation can damage impellers and other components. Bobcat Industrial Air Services recommends identifying the root cause promptly to prevent further damage.
Overheating: Investigate causes of overheating, including inadequate lubrication or misalignment.
Low Flow or Pressure: Check for clogs, worn impellers, or driver issues if flow rate drops.
Excessive Vibration: Misalignment, bearing wear, or mechanical issues can lead to vibrations. Address these promptly to avoid further damage.
Record Keeping
Maintenance Logs
Document all maintenance activities, noting tasks performed, parts replaced, and any issues identified.
Trend Analysis
Use logs to identify patterns in performance, helping to predict future maintenance needs.
Conclusion
By following this Centrifugal Pump Maintenance Checklist and consulting Bobcat Industrial Air Services for expert guidance, you can ensure your pumps operate reliably. Regular maintenance enhances efficiency, reduces downtime, and lowers operational costs. For tailored maintenance solutions, Bobcat Industrial Air Services is your trusted partner in optimizing centrifugal pump performance.
Exploring the Varied Types of Self-Priming Pumps: A Comprehensive Guide
In the intricate world of fluid dynamics and industrial machinery, self-priming pumps have become essential for industries requiring efficient, reliable fluid handling solutions. Bobcat Industrial Air Services in Nashville, TN, provides expertise and solutions in self-priming pump technology to support a wide array of applications, from domestic water supply to complex industrial processes. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the details of self-priming pump technology, explore its mechanisms, examine the different types available, and highlight the factors to consider when selecting the right pump for specific needs.
Purpose of Self-Priming Pumps
At the core of many fluid transfer systems, self-priming pumps stand out due to their ability to lift fluids from lower levels without requiring manual priming. Unlike conventional pumps that need manual intervention, self-priming pumps at Bobcat Industrial Air Services operate autonomously, automatically evacuating air from the suction line to initiate fluid flow. This feature minimizes downtime, improves operational efficiency, and reduces the need for constant supervision, making these pumps indispensable across multiple sectors.
Industries Relying on Self-Priming Pumps
Self-priming pumps have become crucial in various fields, demonstrating their versatility across sectors:
Agriculture: Self-priming pumps streamline irrigation, drawing water efficiently from various elevations.Construction & Mining: On construction sites and in mining operations, these pumps effectively manage dewatering tasks and slurry transfers.Chemical & Pharmaceutical: Precision fluid transfers in the chemical and pharmaceutical industries rely heavily on the accuracy of self-priming pumps.Emergency Services: In firefighting and municipal services, self-priming pumps play a pivotal role in water transfer.Residential Use: Self-priming pumps are also valued for their dependability in providing a steady water supply for homes.
By exploring various self-priming pump types and understanding their mechanisms, industries can make informed decisions. From centrifugal pumps to specialized options like liquid ring and diaphragm pumps, Bobcat Industrial Air Services helps clients identify the best pump for each unique situation.
Types of Self-Priming Pumps
Each type of self-priming pump is designed with specific applications in mind. Here’s an overview of several prominent types and their characteristics:
Standard Self-Priming Centrifugal Pump
This versatile pump type uses centrifugal force to prime itself and is suitable for both domestic and commercial applications. Its design allows it to handle air expulsion efficiently, ensuring consistent fluid flow without the need for external intervention.
Liquid Ring Self-Priming Pump
Known for its safety and durability in volatile environments, liquid ring pumps prevent air intrusion and ensure efficient fluid transfer. Their design makes them ideal for handling gases and vapors, particularly in petrochemical settings.
Diaphragm Self-Priming Pump
Operating on positive displacement, diaphragm pumps offer exceptional precision and chemical resistance, making them invaluable in chemical and pharmaceutical industries.
Trash Self-Priming Pump
With larger passageways, trash pumps are perfect for managing debris-laden fluids and are widely used in construction and wastewater treatment.
Piston Self-Priming Pump
Built for high-pressure applications, piston pumps deliver consistent flow rates in firefighting and irrigation, proving essential in areas requiring reliable, high-pressure performance.
Air-Operated Self-Priming Pump
Ideal for remote locations or hazardous environments, these pumps operate on compressed air, offering explosion-proof performance and corrosion resistance for sensitive applications.
Selecting the Right Self-Priming Pump
When choosing a self-priming pump, several key factors should be considered, including:
Fluid Compatibility: Different fluids require specific pump materials for optimal performance.Application and Industry Requirements: Matching the pump’s capabilities with industry demands ensures optimal efficiency.Flow Rate and Pressure Needs: Understanding the required flow and pressure helps in choosing the right pump type.Maintenance and Serviceability: Routine maintenance is vital for longevity; some pumps may require more frequent servicing based on their design.
Future Trends in Self-Priming Pump Technology
As technology advances, the self-priming pump industry is evolving. Integration with IoT and automation, such as real-time monitoring and remote control, is transforming pump operation. Additionally, energy-efficient designs and improved materials are extending the durability and performance of pumps, supporting industries’ commitment to sustainability and operational excellence.
Conclusion
Self-priming pumps represent a significant advancement in fluid dynamics and industrial applications. With Bobcat Industrial Air Services in Nashville, TN, at the forefront of self-priming pump solutions, clients can expect reliable, innovative products suited to a wide range of requirements. By understanding the unique characteristics of different self-priming pump types, industries can optimize their operations, achieving new levels of efficiency and reliability. Whether handling standard fluids or challenging applications, self-priming pumps stand ready to support the evolving demands of modern industries.